Akrylika Uses, Benefits, and Modern Applications
Akrylika has emerged as one of the most adaptable and widely used materials in modern industries. From contemporary art and interior design to construction and technical manufacturing, it offers a rare combination of clarity, durability, and lightweight performance. As a modern alternative to traditional glass and rigid materials, it supports both aesthetic creativity and functional reliability.
What Is Akrylika and How Is It Defined?
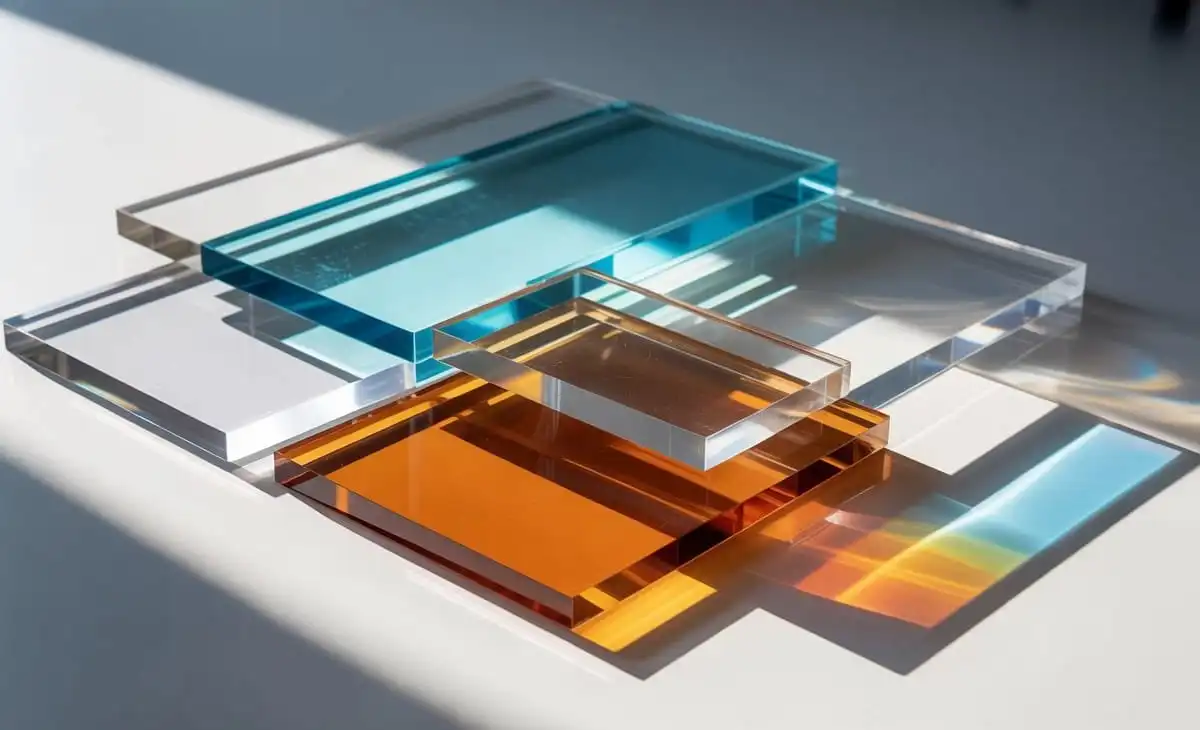
Akrylika refers to acrylic-based materials made primarily from polymethyl methacrylate, commonly known as PMMA. It is valued for its glass-like transparency combined with enhanced strength and flexibility. Unlike glass, it is less prone to shattering and significantly lighter, making it easier to transport and install. These characteristics make it suitable for both decorative and industrial applications where safety, appearance, and durability matter equally.
The Evolution and Development of Akrylika
The development of Akrylika is closely linked to advancements in polymer science during the twentieth century. Early acrylic materials focused mainly on transparency, but later innovations improved impact resistance, UV stability, and fabrication techniques. Over time, it evolved into a multi-purpose material capable of withstanding outdoor exposure and mechanical stress. These improvements allowed it to expand beyond laboratories into architecture, retail, and creative industries.
Optical Clarity and Visual Performance
One of the defining characteristics of Akrylika is its exceptional optical clarity. It allows high light transmission, often matching or exceeding standard glass. This quality makes Akrylika ideal for displays, windows, signage, and artistic installations. Its clarity remains stable over time when proper UV-resistant grades are used, ensuring long-lasting visual appeal even in bright or outdoor environments.
Strength, Lightweight Nature, and Durability
Akrylika offers impressive strength while remaining significantly lighter than glass. This balance reduces structural load and installation complexity. Its impact resistance enhances safety, especially in public spaces or high-traffic environments. Because it does not shatter easily, it is widely used where durability and user protection are critical without sacrificing transparency or aesthetics.
Fabrication Flexibility and Customization Options
It can be easily cut, drilled, bent, molded, and polished using standard fabrication tools. This flexibility supports creative freedom and technical precision. Designers and manufacturers can customize thickness, shape, color, and finish according to project requirements. This adaptability allows Akrylika to serve both simple functional purposes and highly complex design concepts.
Applications of Akrylika Across Industries
It is used in a wide range of industries due to its versatile properties.
- Art and Creative Design
Artists and designers use Akrylika for sculptures, installations, display cases, and decorative elements due to its clarity and formability. - Interior Design and Architecture
It is widely applied in partitions, furniture, lighting features, wall panels, and modern architectural accents.
These uses demonstrate how it bridges artistic expression with structural practicality.
Industrial and Commercial Use Cases of Akrylika
Beyond creative fields, it plays a major role in industrial and commercial environments.
- Technical and Industrial Settings
It is used in machine guards, laboratory equipment, protective barriers, and aquariums. - Retail and Branding Applications
Retail displays, signage, and promotional stands rely on Akrylika for a clean and professional presentation.
These applications highlight its reliability in demanding conditions.
Benefits of Using Akrylika Material
It offers multiple advantages across different use cases. It provides visual elegance while maintaining strength and safety. Its shatter-resistant nature reduces injury risk compared to glass. The material is also cost-effective due to lower transportation costs and ease of fabrication. Additionally, it adapts well across industries, making it a practical long-term investment for both small and large projects.
Limitations and Challenges of Akrylika
Despite its advantages, it has certain limitations. It is more susceptible to surface scratches than glass, requiring careful handling. High temperatures can cause deformation if not properly managed. Maintaining optical clarity also demands appropriate cleaning methods. Understanding these challenges helps users choose the correct grade and application method for optimal results.
Real-World Example of Akrylika in Use
A modern retail store redesigned its product displays using Akrylika panels instead of glass. The switch reduced installation costs, improved safety, and allowed customized shapes that enhanced brand presentation. Over time, the displays maintained clarity and durability, demonstrating how it delivers both functional and aesthetic value in real commercial environments.
Emerging Trends and Future of Akrylika
The future of Akrylika is shaped by innovation and sustainability. Manufacturers are developing eco-friendly and recyclable variants to reduce environmental impact. Integration with smart lighting, digital displays, and interactive surfaces is increasing in modern architecture. Custom fabrication technologies are also expanding, enabling highly personalized Akrylika solutions for creative industries.
Conclusion
Akrylika stands as a vital material in modern design, art, and industrial applications. Its combination of transparency, strength, and adaptability allows it to replace traditional materials while offering enhanced safety and flexibility. As sustainable production and smart integration continue to advance, it will remain a key contributor to creative and functional solutions for years to come.