185.63.2253.200: Invalid IP Explained
The term 185.63.2253.200 might look like a typical internet address at first glance, but it isn’t what it seems. Unlike real IPs that connect devices on networks, this number sequence breaks key addressing rules used for internet communication. In networking and cybersecurity discussions, 185.63.2253.200 has sparked confusion, curiosity, and even concern among users who stumble upon it in logs or reports. Understanding why this number is invalid—and what its appearance might suggest—is essential for anyone working with networks, logs, or online security.
What Is 185.63.2253.200?
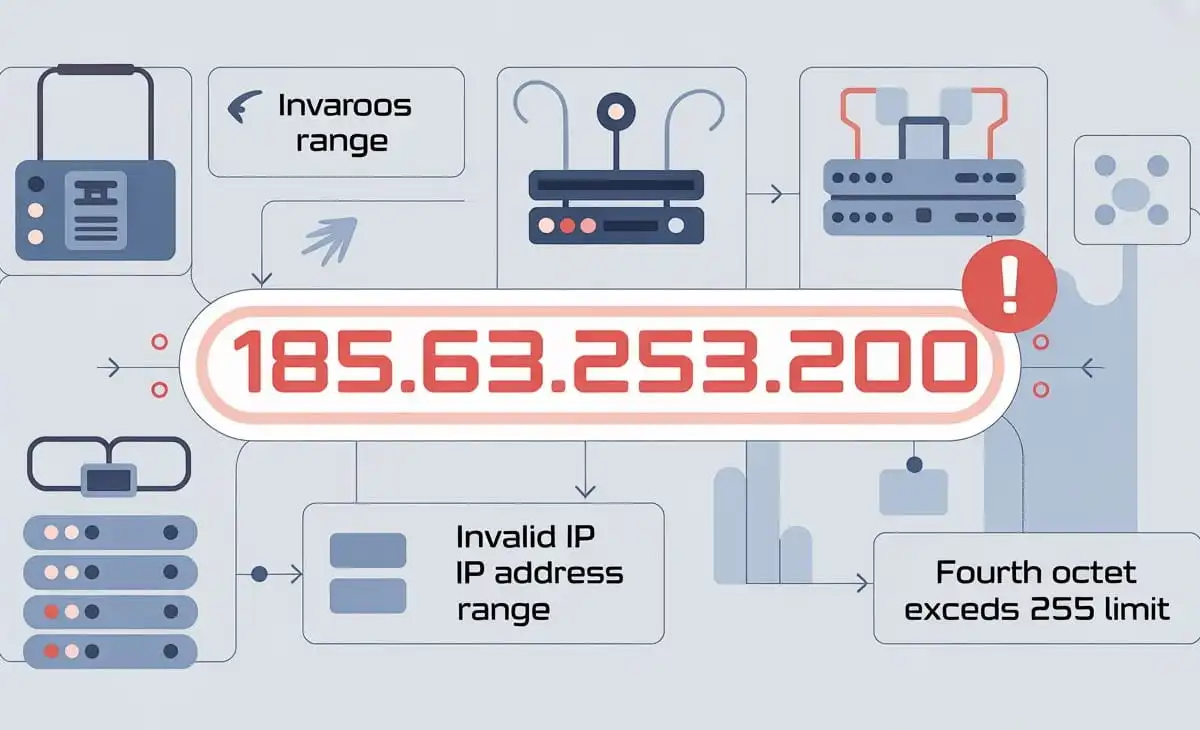
In simple terms, 185.63.2253.200 looks like an IP address at first glance because it has four numbers separated by dots. But one of the key rules of standard IP addresses—specifically IPv4 addresses—is that each segment must be between 0 and 255. In 185.63.2253.200, the third section (2253) far exceeds this limit, making it impossible for this string to function as a real IPv4 address on the internet.
The Rules of IPv4 Addressing
All IPv4 addresses consist of four groups of numbers, called octets. Each octet must be a value from 0 to 255 because they are made up of 8 bits in binary form. This structure is what allows networks to route data correctly between devices. When any one of those segments goes beyond 255—as happens in 2253—the entire format becomes invalid. Therefore, 185.63.2253.200 can’t be assigned to any device, server, or network interface using IPv4 addressing.
Why 185.63.2253.200 Doesn’t Exist in Real Networks
Since IPv4 standards strictly enforce numeric limits for each segment, systems like routers, servers, and firewalls automatically reject malformed addresses such as 185.63.2253.200. Networking software and hardware won’t recognize this string as a destination or source address. Instead, it’s treated as corrupted or invalid data. This means that no computer or phone anywhere on the public internet can communicate using this exact sequence.
How Does 185.63.2253.200 Appear Online?
Even though it’s not a valid address, 185.63.2253.200 does show up in certain places:
- Typographical errors: Someone may accidentally type extra digits when copying a real address.
- Log corruption: Garbled data from software bugs can create invalid strings.
- Automated scripts: Bots or poorly written tools may generate strange patterns.
- Testing placeholders: Developers often insert fake data when testing systems.
These scenarios explain why a number that can’t exist on the internet still ends up in server logs or analytics reports.
The Difference Between Real and Fake IPs
To grasp why 185.63.2253.200 is invalid, it helps to compare it with a real IP. For example, 185.63.225.200 is a perfectly valid IPv4 address because all four segments are within the allowed range. In contrast, the “2253” in your keyword quadruple is far above 255 and thus breaks the IPv4 rules. This distinction is critical for network administrators and security analysts who regularly debug traffic logs or manage firewall rules.
Why People Search for 185.63.2253.200
Strangely enough, 185.63.2253.200 has attracted attention online. Here are key reasons why people might look it up:
- Confusion from seeing it in logs
- Misunderstanding the IP format
- Curiosity about unusual numeric patterns
- Content or SEO tactics that insert random numeric strings
This mix of misunderstanding and curiosity has made the invalid IP somewhat of an online phenomenon. It’s important to approach it with skepticism and technical clarity rather than assuming it’s harmful on its own.
The Cybersecurity Angle of Invalid IP Addresses
Encountering an invalid address like 185.63.2253.200 might seem harmless, but it can matter in cybersecurity contexts. Attackers sometimes use fake or malformed data to confuse defensive tools or hide their real origins. For example, they may inject malformed IP strings into logs or headers to evade filtering systems that aren’t properly configured to validate inputs. While the address itself isn’t functional, its presence can be a sign that you need to investigate further for suspicious activity.
How to Handle This When It Shows Up
If you find 185.63.2253.200 in your logs or analytics, here are practical steps:
- Run an IP validator: Tools can instantly flag malformed addresses.
- Check surrounding log entries: Look for patterns indicating bot traffic.
- Update firewall rules: Ensure malformed request filtering is enabled.
- Investigate the source: If it’s repeated, it might signal automated scanning or misconfigured tools.
These best practices help maintain secure and accurate reporting in your network systems.
Case Study: Debugging Malformed Entries in Logs
A medium-sized business once noticed unusual traffic records showing entries like 185.63.2253.200 in their server logs. Initially, IT staff assumed it was a threat and spent hours tracing each occurrence. After deeper analysis, they discovered it was caused by a log-parsing script that concatenated numbers incorrectly due to a formatting bug. By fixing the script and validating inputs, they eliminated the malformed entries and improved log accuracy. This real case illustrates the importance of not assuming danger based solely on malformed entries—and to always verify their source carefully.
Conclusion
To summarize, 185.63.2253.200 is not a valid IPv4 address because one of its numeric segments exceeds the maximum allowable range. Its appearance in logs or online content usually stems from typos, corrupted data, placeholder values, or automated tools. While the string itself isn’t harmful, its presence can signal deeper issues that merit investigation. Learning how to recognize invalid addresses like this helps tech professionals maintain network integrity and improve cybersecurity awareness.